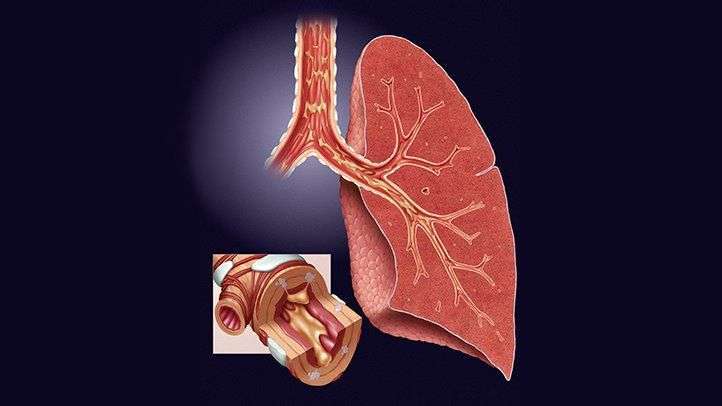
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that carry air to the lungs. It can be either acute or chronic.
- Acute Bronchitis:
- Causes: Acute bronchitis is often caused by viral infections, commonly the same viruses responsible for colds and the flu. Bacterial infections can also lead to acute bronchitis.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include coughing with or without the production of mucus, chest discomfort or pain, fatigue, and sometimes low-grade fever.
- Treatment: Acute bronchitis is usually self-limiting and often resolves on its own within a few weeks. Treatment may involve rest, staying hydrated, and using over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections but may be prescribed if a bacterial infection is suspected.
- Chronic Bronchitis:
- Causes: Chronic bronchitis is typically associated with long-term exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, or industrial dust and chemicals.
- Symptoms: Symptoms are similar to acute bronchitis but persist for longer periods (at least three months over two consecutive years). Chronic bronchitis is a type of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
- Treatment: Management involves quitting smoking if applicable, avoiding exposure to lung irritants, using bronchodilators and inhaled corticosteroids, and pulmonary rehabilitation. Oxygen therapy may be necessary in advanced cases.
Common Symptoms of Bronchitis:
- Persistent cough, which may produce mucus (sputum)
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Chest discomfort or pain
- Slight fever and chills
Preventive Measures:
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking is a significant risk factor for developing chronic bronchitis. Quitting smoking can help prevent and manage the condition.
- Limit Exposure to Irritants: Reduce exposure to air pollutants, chemicals, and other lung irritants.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands regularly to reduce the risk of viral infections that can lead to acute bronchitis.
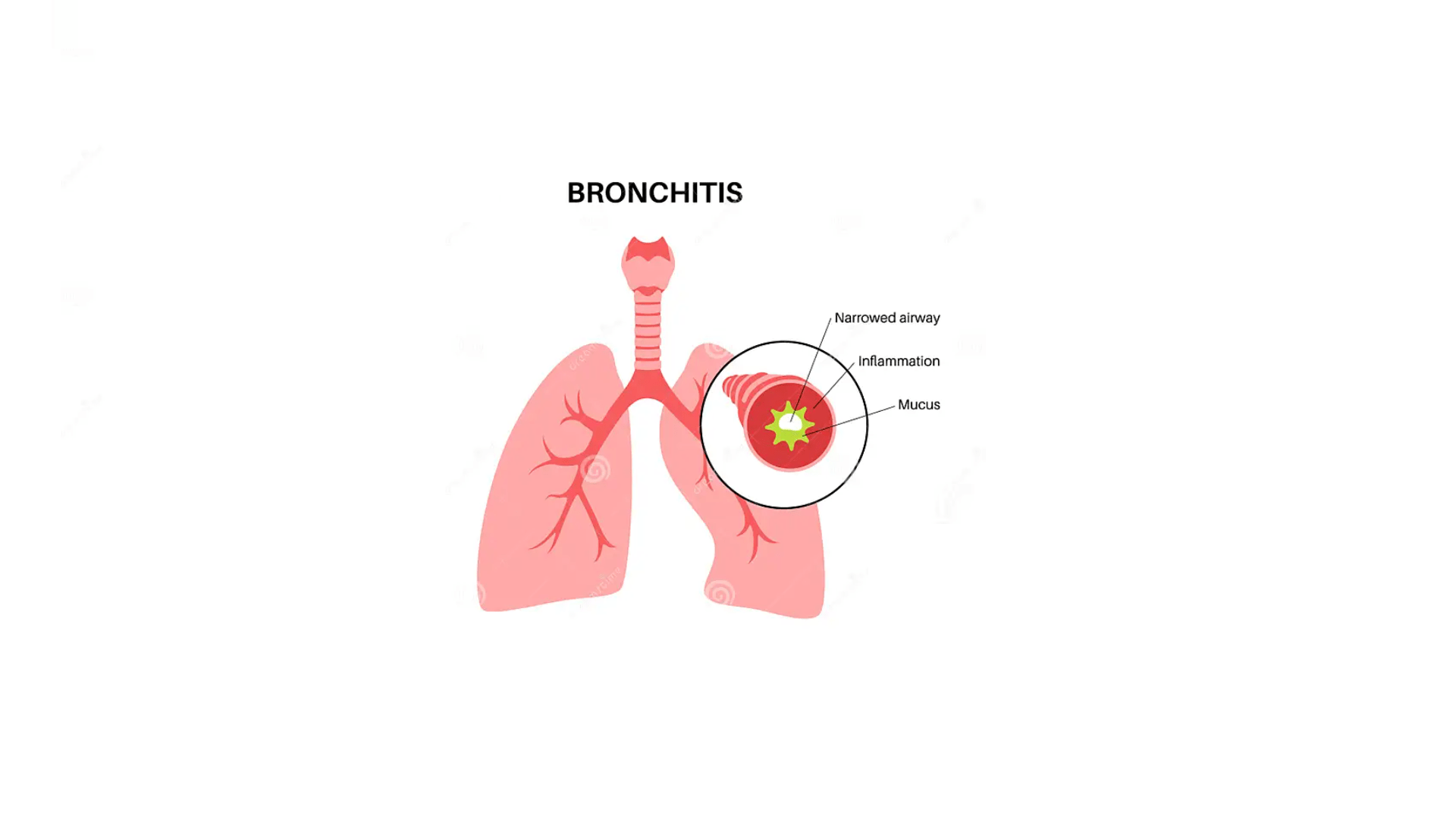
If you suspect you have bronchitis, especially if symptoms persist or worsen, it's essential to seek medical advice. A healthcare professional can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment based on the specific type of bronchitis and its underlying causes.
Top Social Media Groups for Business, Professional Networking, Promotions, Jobs, Spiritual, Marketing, Visa
Click here to join Unlimited Groups
News, Health, Travel, Jobs, Top Trending, Top Viral & Entertainment. Follow Us on Social Media
Telegram: Infimor | Instagram: Infimor | Facebook: Infimor LinkedIn: Infimor | YouTube: Infimor
KK