Cyber security is currently one of the most in-demand careers in the IT industry. As the need to get things online grows, so does the demand. It also raises the major concern for the industry of securing data assets to prevent data misuse. The rise in cybercrime has made major corporations vulnerable, compelling them to hire Cyber Security professionals such as Cyber security Engineers and Cyber security analysts to protect company assets and ensure business success. As a result, you can capitalize on this market trend and become a Cyber Security expert. To prepare for the interview, go over the top 50 Cyber Security interview questions and answers.

- What exactly is cryptography?
- What exactly is traceroute? Mention its applications.
- What exactly is a three-way handshake?
- What exactly is a response code? Make a list.
- What exactly is the CIA triad?
- What are the most common types of cyberattacks?
- What exactly is data leakage?
- What exactly is a firewall and why is it used?
- Describe port scanning?
- Describe brute force attacks and how to avoid them?
- What's the distinction between hashing and encryption?
- What is the distinction between vulnerability assessment and penetration testing?
- Describe how to set up a firewall.
- What exactly is SSL encryption?
- How are you going to secure a server?
- What exactly is cryptography?
Cryptography helps to protect information from third parties known as adversaries. Only the sender and recipient have secure access to the data.
2. What exactly is traceroute? Mention its applications.
Traceroute is a network diagnostics application. It aids in the tracking of a packet's path across an IP network. It displays the IP addresses of all routers that it pings between the source and destination.
Uses It shows the time taken by the packet for each hop during the transmission. When the packet is lost during the transmission, the traceroute will identify where the point of failure is.
3. What exactly is a three-way handshake?
It is a process that occurs in a TCP/IP network when a connection is established between a local host and the server. Before communication can begin, a three-step process is used to negotiate packet acknowledgment and synchronization.
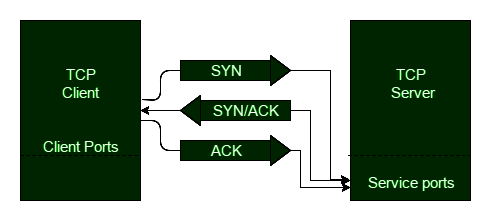
Step 1: The client uses SYN to connect to the server.
Step 2: The server sends SYN+ACK in response to the client's request.
Step 3: The client responds to the server's response with an ACK, and data transmission begins.
4. What exactly is a response code? Make a list.
HTTP response codes indicate a server’s response when a client makes a request to the server. It shows whether an HTTP request is completed or not.
1xx: Informational
The request is received, and the process is continuing. Some example codes are:
100 (continue)
101 (switching protocol)
102 (processing)
103 (early hints)
2xx: Success
The action is received, understood, and accepted successfully. A few example codes for this are:
200 (OK)
202 (accepted)
205 (reset content)
208 (already reported)
3xx: Redirection
To complete the request, further action is required to take place. Example codes:
300 (multiple choice)
302 (found)
308 (permanent redirect)
4xx: Client Error
The request has incorrect syntax, or it is not fulfilled. Here are the example codes for this:
400 (bad request)
403 (forbidden)
404 (not found)
5xx: Server Error
The server fails to complete a valid request. Example codes for this are:
500 (internal server error)
502 (bad gateway)
511 (network authentication required)
5. What exactly is the CIA triad?
The CIA Triad is a security model that is used to ensure IT security. The acronym CIA stands for confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility.
Confidentiality: To prevent unauthorised access to sensitive information.
Integrity: The protection of data from unauthorised deletion or modification.
Availability: To confirm the data's availability whenever it is required.
6.What are the most common types of cyberattacks?
Here is a list of common cyber attacks aimed at causing system damage.
- Man in the Middle attack: The attacker inserts himself between the sender and the receiver's communication. This is done to eavesdrop and impersonate someone in order to steal data.
2. Phishing: In this case, the attacker will pose as a trusted entity in order to obtain sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers.
3. Rogue Software: A phishing attack in which the attacker pretends to be a virus on the target device and offers an anti-virus tool to remove the malware. This is done to infiltrate the system with malicious software.
4. Malware: Malware is software that is intended to attack the target system. The software could be a virus, worm, ransomware, spyware, or something else.
5. DDoS: This is used to flood the target network with massive traffic, rendering the website or service inoperable.
6. Malvertising: Malvertising is the injection of malicious code into legitimate advertising networks, causing users to be redirected to unintended websites.
Password Attacks: As the name implies, the cyber hacker cracks credentials such as passwords.
7.What exactly is data leakage?
The unauthorised transmission of data from an organisation to an external recipient is referred to as data leakage. Electronic, physical, web, email, mobile data, and storage devices such as USB keys, laptops, and optical media can all be used as modes of transmission.
Data leakage types include:
Accidental leakage occurs when an authorized entity accidentally sends data to an unauthorized entity.
Malicious insiders: An authorized entity sends data to an unauthorized entity on purpose.
Electronic communication: Hackers use hacking tools to gain access to the system.
8.What exactly is a firewall and why is it used?
To protect data privacy, a firewall is a network security device/system that blocks malicious traffic such as hackers, worms, malware, and viruses.
Uses:
It keeps track of both incoming and outgoing network traffic. It only permits or allows data packets that comply with a set of security rules.
It serves as a firewall between the internal network and incoming traffic from outside sources such as the Internet.
9. Describe port scanning?
A port scan can help you determine which network ports are open, listening, or closed. Administrators use this to test network security and the strength of the system's firewall. It is a popular reconnaissance tool for hackers to identify weak points in a system in order to break into it.
Some examples of basic port scanning techniques are:
UDP
Ping scan
TCP connect
TCP half-open
Stealth scanning
10. Describe brute force attacks and how to avoid them?
A brute force attack is a hack in which the attacker uses trial and error to guess the target password. It is mostly implemented using automated software to login with credentials.
Here are some methods for avoiding a brute force attack:
Create a long password.
Create a complex password.
Set a maximum number of login failures.
11. What's the distinction between hashing and encryption?
Hashing
A one-way function in which the original message cannot be decrypted.
Used to verify data
Used to send files, passwords, etc. and to search
Encryption
Encrypted data can be decrypted to the original text with a proper key.
Used to transmit data securely
Used to transfer sensitive business information
12. What is the distinction between vulnerability assessment and penetration testing?
Vulnerability Assessment (VA)
Vulnerability Assessment (VA) and Penetration Testing (PT) identify network vulnerabilities.
Indicates how vulnerable the network is.
When there is a change in the system or network, this is done at regular intervals.
Penetration Testing (PT)
Identifies vulnerabilities in order to exploit them in order to gain access to the system.
Determines whether the discovered vulnerability is genuine.
When there are significant changes to the system, this is done once a year.
13. Describe how to set up a firewall?
The steps for installing a firewall are as follows:
- The steps for installing a firewall are as follows:
- Username/password: Change the default password of a firewall device.
- Remote Administration: Always turn off the Remote Administration feature.
- Configure appropriate ports for the web server, FTP, and other applications to work properly.
- Disable the DHCP server when installing a firewall to avoid conflicts.
- Logging: Enable logs to view firewall troubleshoots and logs.
- Policies: Set up strict security policies with the firewall.
14. What exactly is SSL encryption?
Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is a security protocol used for encryption. It ensures network privacy, data integrity, and authentication, similar to online transactions.
The steps for configuring SSL encryption are as follows:
- The steps for configuring SSL encryption are as follows:
- A browser establishes a connection to an SSL-secured web server.
- In exchange for its own private key, the browser requests the server's public key.
- If it is reliable, the browser requests an encrypted connection with the web server.
- The acknowledgment is sent by the web server to initiate an SSL encrypted connection.
- SSL communication between the browser and the web server begins.
15. How are you going to secure a server?
To protect data from unauthorised access, a secure server employs the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol to encrypt and decrypt data.
The four steps to securing a server are as follows:
Step 1: Set a password for the root and administrator users.
Step 2: Create new system administrators.
Step 3: Do not grant administrator/default root accounts remote access.
Step 4: Set up firewall rules to allow remote access.
